Obesity in India is defined as body mass index [BMI: Weight (kg)/ Height (m)2] more than 27.5 kg/m2 (normal BMI is between 18 to 23 kg/m2) and people with BMI more than 32.5 kg/m2 and 37.5 kg/m2 are defined as severely obese and morbidly obese respectively. Obesity is a chronic disease with accumulation of excessive body fat and subsequent risk for development of medical conditions like diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HT), obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), degenerative joint disease, hyperlipidemia (HPL), hyperuricemia, fatty liver, depression, polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD) and asthma to name a few. Thus obesity adversely affects all the organs and lead to constellation of symptoms referred to as Metabolic Syndrome of Obesity. People with morbid obesity (BMI > 37.5 kg/m2) have 50% to 100% higher mortality rates. There is also emotional effect of obesity where obese patient suffers neglect from society and thus are prone to develop mental symptom like depression, anxiety and eating disorders. So Bariatric surgery or weight loss surgery or metabolic surgery is a life style modification surgery which not only reduces weight but through its hormonal effect it cures/ controls the medical conditions associated with it. Its effect on glucose control and other metabolic problems is striking, which can be seen soon after the procedure and even before there is significant reduction in weight.
Bariatric surgery is indicated if a patient is morbidly obese (BMI > 37.5 kg/m2) or severely obese (BMI > 32.5 kg/m2) with seriously related diseases like DM, HT, OSA and others as explained above. It can be safely done in patients between 18 to 65 years of age who have failed weight loss alternatives like dieting, exercise and behavior modification programs and who are committed to healthy life style. The patient not only reduces extra fat but many obesity related conditions like Diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, heart diseases are resolved or significantly improved. PCOD and resulting infertility is also greatly improved. Patient can become pregnant after 18 months to 2 years after surgery and Overall quality of life is improved in 95% of patients and mortality is reduced in 89% of patients.
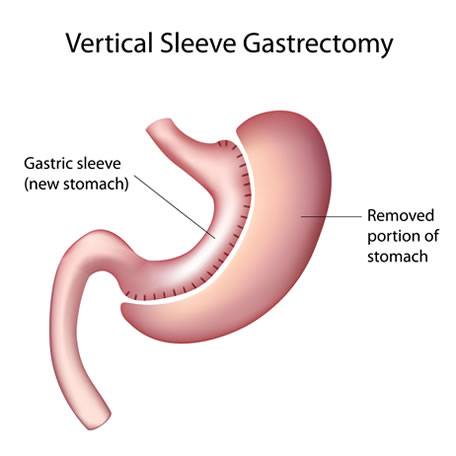
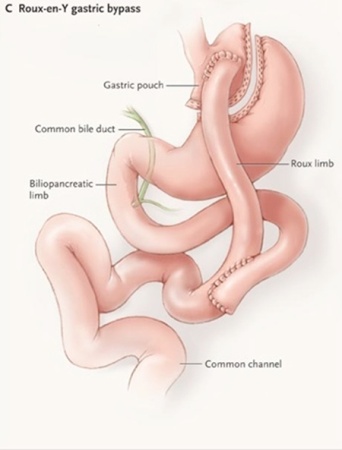
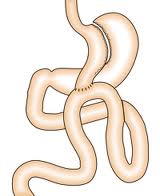
There are various ways for doing bariatric surgery like Sleeve gastrectomy which restricts the food intake and Gastric Bypass (Roux- en-y and Mini Gastric Bypass) which also limits the absorption of ingested food. All the bariatric surgeries are done laparoscopically by making several small incisions (4 to 6) ranging from 5 to 15mm, through which the surgeon inserts laparoscopic instruments to perform the surgery. Patients usually go home two to three days after surgery. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (Fig 1) is accomplished by cutting away the outer portion of the stomach, leaving a small tube or sleeve of stomach. This reduces the stomach volume by about 80%. The stomach is now like a hockey stick shaped organ, which holds less food and produces less acid. In addition, the part of the stomach that produces the hormone implicated in hunger (Ghrelin) is also removed and therefore there is a component of appetite suppression. In Laparoscopic roux en y gastric bypass (Fig 2), a small stomach pouch (25-30 ml) is created with a stapler device, and connected to the distal small intestine. The upper part of the small intestine is then reattached in a Y-shaped configuration. Laparoscopic Mini Gastric bypass (Fig 3) consists of forming a long gastric tube and attaching it 200 cm down to small bowel with single anastomosis. Unlike conventional gastric bypass it has fewer early and long term complications and can achieve weight loss similar to it. The disadvantage is bile reflux which is mentioned but practically very few patients observe it.
Nowadays with the advent of new stapling devices, the risks associated with the procedure are negligible and are like any other laparoscopic surgery. Patient can go home after 2 to3 days and start their routine work after 1 week and strenuous activity after 6 weeks. The diet after surgery goes through various phases starting from all liquid diet to semisolid to complete diet over 6 to 8 weeks. The complete diet is small in amount and has to be taken more frequently and food has to be chewed properly and patient has to avoid intake of water, liquids 30 minutes before and after meals. The striking control of Diabetes is seen soon after the surgery and even before any significant weight loss. The theories suggested are diet control immediately after surgery as patient is on liquid sugar free diet and hormonal changes (Ghrelin and Integrins) which produce satiety and have similar actions like insulin. Also when person reduces weight they are more mobile and whatever Insulin they are producing works better as there is reduction in Insulin resistance. Also the weight loss produced is sustainable and it has been shown that surgery improves patient’s desire and dedication for a healthy and better life. Apart from change in appearance, surgery brings new hope, improves self confidence and positivity in patient’s thought process. Thus this surgery changes life style and gives new unimaginable dimensions to life.







